Web 2.0 once was an unbelievable leap in internet evolution that destroyed boundaries enabling billions of people to share their opinions, work, and lives in general. Nonetheless, thus far, it has run its course, compromised by privacy risks and violations of free speech.
Now, mankind is at the dawn of a new internet era that will give internet users the right to be in charge of the information they share without any web monopolists dictating the rules and capitalizing on user data. The concept of Web 3.0 is getting louder every day, and the advantages it offers in web security and personalization of web experience are breathtaking. In this post, we will talk about the Web 3.0 definition and examples, its advantages against Web 2.0, and the impact it will have on business and regular users.
Web 3.0 definition
Web 3.0 is a new concept of the internet that will supersede web 2.0, bringing advanced artificial intelligence, machine learning, and ultra-secure blockchain algorithms to the table.
AI- and ML-powered web 3.0 technologies that can understand complex queries and learn from users’ internet habits, will be able to provide more relevant and tailor-made content. This, in turn, makes interactions with smart gadgets more human-like. Decentralization and blockchain, on the other hand, will make virtual communication safer, preserving privacy.
Another fantastic feature of Web 3.0 is its unrestricted availability and ubiquity enabled by a growing number of smart devices connected through the internet (IoT). You can already get a taste of Web 3.0 freedom by using a digital assistant for connecting with a security system, climate control, or other devices in a smart home.
Today, web 3.0 examples include decentralized data storage (you may like Storj), super-secure banking/insurance apps (Everledger is a great example), messaging (like e-Chat), social networks (check out Steemit), digital libraries (LBRY is a must-try), and so forth.
However, the easiest way to get Web 3.0 explained is through the example of a virtual assistant. Powered by voice recognition (which is, by the way, one of the fundamental web 3.0 tools), Apple’s Siri, for instance, can provide tailor-made recommendations for the user’s queries, be it setting up meetings, adding items to the grocery list, booking flight tickets, or finding a perfect place to dine out.
A short history of the Web from Web 1.0 to Web 3.0
To better understand Web 3.0 meaning and benefits, we should recollect how the internet evolved up to our days:
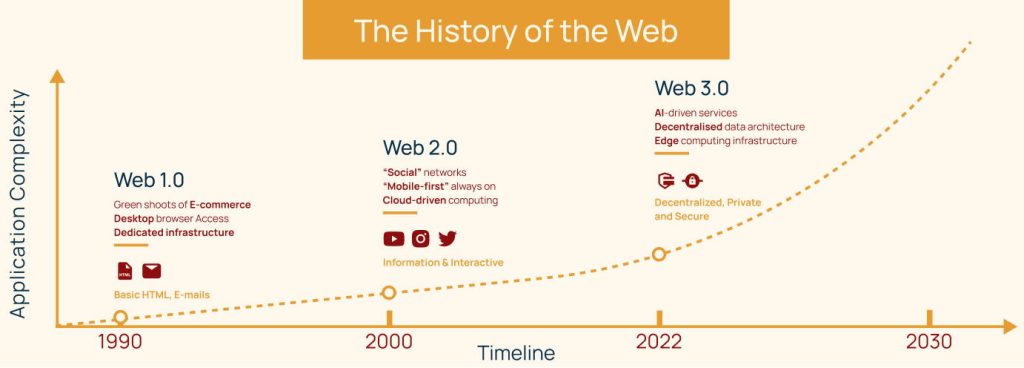
- Web 1.0 (also described as the “read-only” internet) began its virtual expansion in 1989. Users could find necessary information only if they had the exact website URL as no search engines existed back then.
- Web 2.0 (also known as the “read-and-write” internet) started in the mid-2000s from the rise of social media that enabled users to not only read but also produce content and interact by liking, sharing, commenting, messaging, etc. We know it for the rapid spread of smart camera phones, mobile internet, and cloud solutions that jumpstarted blogging, bulk video content, and eCommerce. Nonetheless, we paid for the privilege of our privacy. Web 2.0 eventually turned into Big Brother, and he’s watching us, collecting and analyzing our data, tracking our buying habits, finances, locations, etc.
- Web 3.0 (AI-powered, interactive, “read-and-write” internet) naturally evolves from the previous two models of the internet and leverages decentralization for neutralizing the “Big Brother” controlling authority, artificial intelligence for a more personalized web experience, and blockchain for enhanced data security. The term “web 3.0” was first introduced back in 2006, but it’s 2022 already, and web 3.0 is still far from being globally adopted.
The full launch of Web 3.0 is hindered by technical challenges. Web 3.0 technologies require not only more powerful and advanced devices but also more tech-savvy users. Privacy laws and user data usage psychology must also mature to fit the new internet concept.
What is the difference between Web 2.0 and Web 3.0?
The second and the third generations of the web have much in common because Web 3.0 doesn’t entirely nullify the pillars of Web 2.0 (such as mobile web or cloud technologies) but rather “fixes” them using new approaches. This table shows the difference between Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 and the benefits of the latter.
| Web 2.0 | Web 3.0 |
|---|---|
| Centralization and non-transparent data policy: ● Huge web authorities (such as Google, Microsoft, Meta, Apple, etc.) dictate the terms of use, fully control content management, and take advantage of user data, which causes privacy issues. ● The central controlling authority defines what can be published and what not, putting free speech at risk. | Transparency and decentralization: ● Decentralized, pear-to-pear networks combine data from various data providers (users), preserving their ownership of the data and content. ● There are no web entities that approve, define, or stop interactions. ● Unrestricted and non-discriminatory access to content. |
| Jeopardized internet security: ● More anonymous web 2.0 gave rise to cybercrime in the forms of identity theft, harassment, cyberbullying, sharing false information, etc. ● Tech giants fail to protect user data. | Advanced data security: ● Blockchain technology enables sound data encryption and fast and safe transactions without intermediaries. ● Mitigated risk of hacking. ● Tech firms cannot steal our individual information and leverage it to gain profit, which allows us to monetize our data as we see fit. |
| Slack, human-optimized web experience: ● Content must be heavily optimized with keywords by the writers to match a particular user query. ● Frequent fraudulent behaviors: rating manipulations, jug-handled product feedback, etc. | Faster, more accurate, and intelligent search results: ● Web 3.0 better understands even complex user search queries and grasps the intents behind them to provide more relevant and personalized answers in an instant. ● AI-driven search, one of the most prominent web 3.0 features, learns from its users and forecasts their demands. ● Flexible websites powered by artificial intelligence solutions adjust their form and content to cater to the needs of every user. |
What impact will Web 3.0 have on your business?
- Web 1.0-style websites will die. In the Web 3.0 era of mega-personalized web experience, it will be impossible to retain an audience relying on rigid, old-fashioned websites. Companies who want to blow past competition should consider revamping their online presence using advanced AI and blockchain technologies.
- Higher vulnerability to reputational damage. Since Web 3.0 will make all information easily accessible and less anonymous, businesses will need to take heart and get ready for reputational issues to survive in this new transparent web. They should invest in top-notch, highly-personalized engagement with their customers rather than old-fashioned Web 2.0 corrupt web techniques.
- Businesses need to upgrade their hardware. To be in the lead and benefit from tremendous web 3.0 personalization and security, businesses will need to invest in cutting-edge computers able to support the latest AI and blockchain solutions. So only technically savvy businesses with technically savvy customers will be able to keep up, at least for a little while longer.
Web 3.0 is almost here, but… who is ready for it?
A safe and restriction-free internet that learns and thinks to please your even unspoken queries sounds like a far-far-away future. However, artificial intelligence, machine learning, and blockchain solutions already prepared the ground for it. The challenge remains: will big businesses be ready to discard their shady data policies to embrace equality, openness, and transparency?





